Luxury Economy: Do You Know the Veblen Effect?
Chairman LUXONOMY™ Group
Introduction
The Veblen Effect is a fascinating phenomenon that challenges the basic principles of traditional economics, demonstrating how the demand for certain goods can increase with their price. This extensive article delves deeply into this intriguing concept, introduced by economist and sociologist Thorstein Veblen in his work “The Theory of the Leisure Class” published in 1899. From its theoretical foundations to its implications in the modern economy, through its manifestation in marketing and its social and cultural impact, this detailed analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the Veblen Effect.
Theoretical Foundations
Thorstein Veblen and His Contribution
Thorstein Veblen, born in 1857, was an economist and sociologist known for his criticisms of classical economics and his keen observation of the social dynamics of his time. In “The Theory of the Leisure Class,” Veblen analyzed how the upper classes used conspicuous consumption and leisure to display their social status. He introduced the concept of “conspicuous consumption,” which refers to spending on luxury goods and services as a way to display wealth and status. According to Veblen, these goods are valued not only for their intrinsic utility but also for their ability to signal their owners’ social position.
Definition of the Veblen Effect
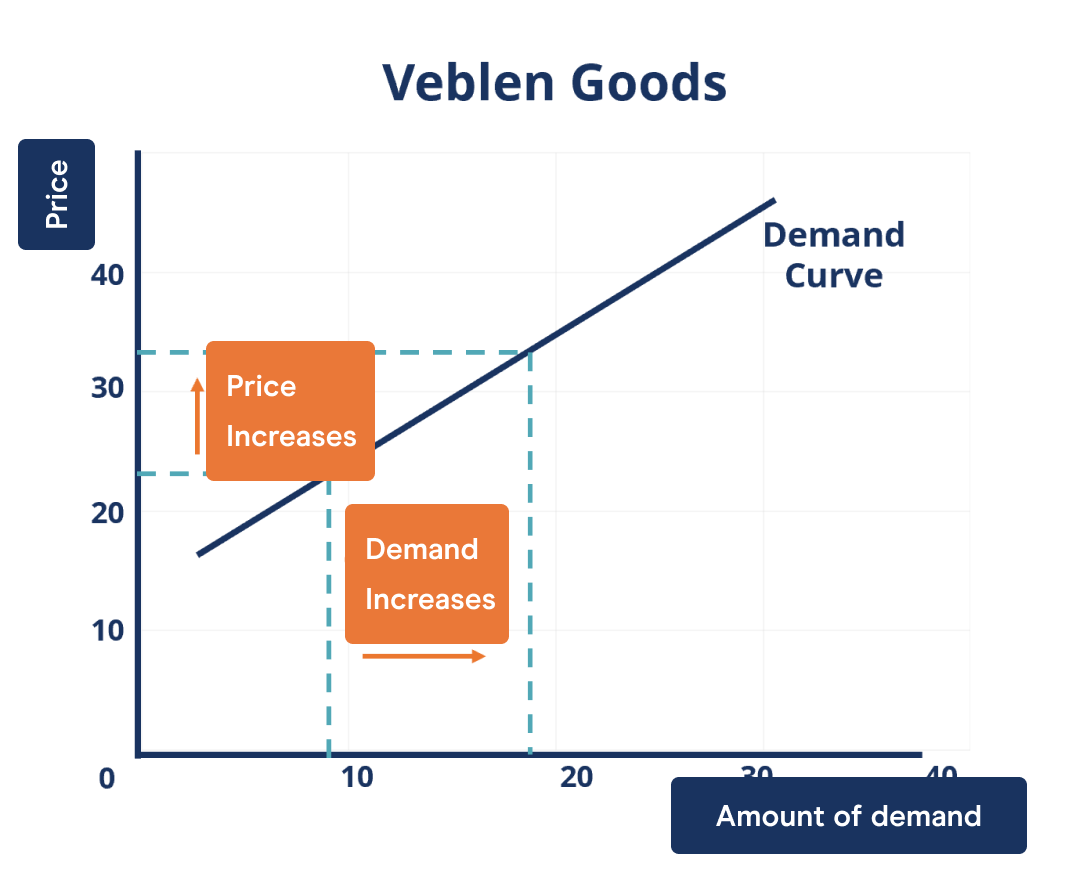
The Veblen Effect refers to a situation where an increase in the price of a good leads to an increase in its demand due to its appeal as a status symbol. This contrasts with the law of demand, which holds that as the price of a good increases, its demand decreases. In the context of the Veblen Effect, the high price of a product contributes to its appeal, as consumers perceive it as a sign of exclusivity and prestige.
Manifestations of the Veblen Effect
Luxury Markets
The Veblen Effect is most evident in luxury goods markets. Jewelry, haute couture fashion, luxury cars, exclusive watches, and high-value real estate are typical examples. These products are perceived as symbols of social status and prestige. A designer handbag, an exclusive brand sports car, or a mansion in a coveted location are examples of goods that can experience the Veblen Effect.
Global Luxury Goods Market Sales (in billions of euros)
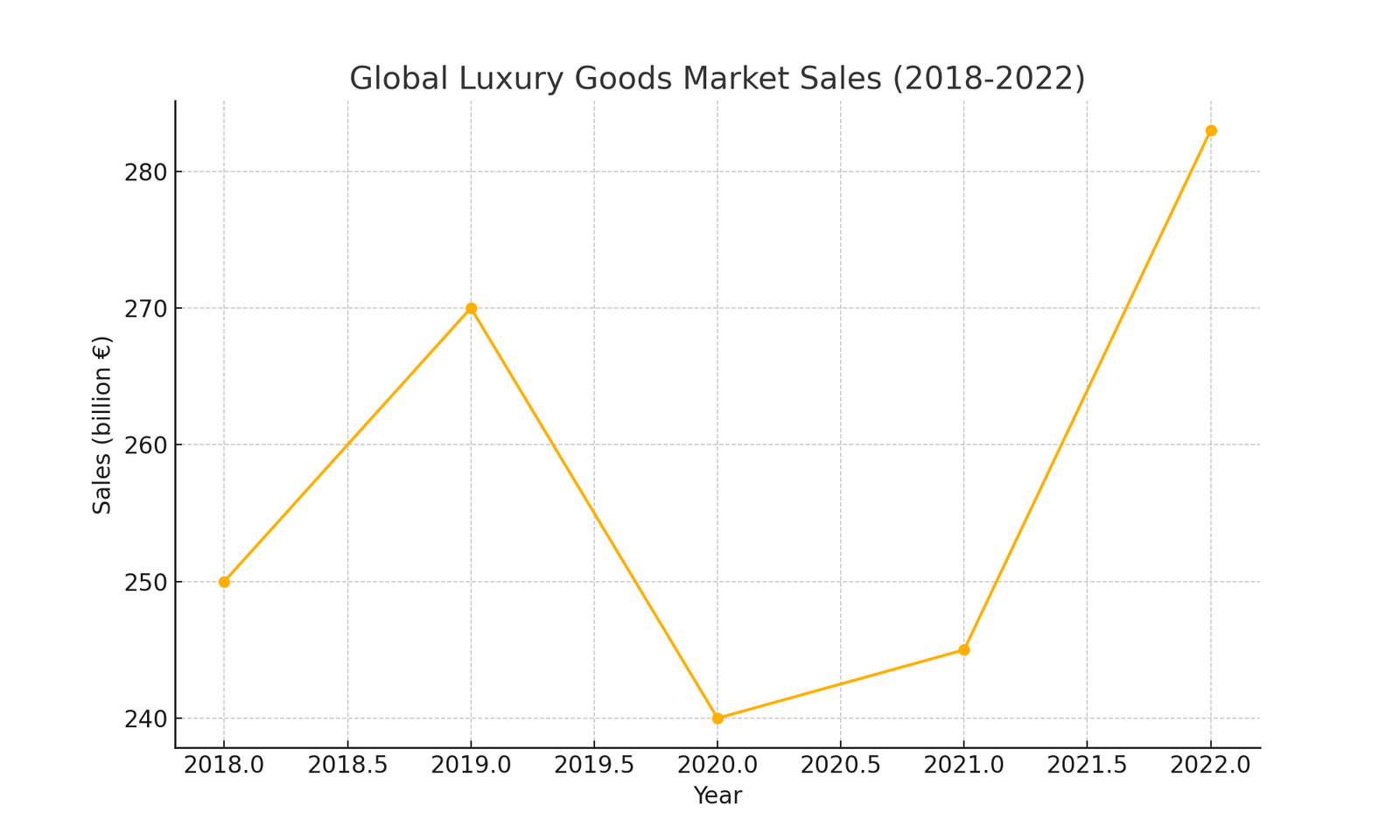
For example, a study by Bain & Company in 2022 estimated that the global luxury goods market reached 283 billion euros, with a 15% growth compared to the previous year. Brands like Louis Vuitton, Gucci, and Hermès reported increased sales despite raising the prices of their products. This phenomenon illustrates how the price increase of these items does not deter buyers but often makes them more desirable.
Conspicuous Consumption and Social Media
In the age of social media, conspicuous consumption has found a new platform to display itself. The ostentation of luxury goods on platforms like Instagram and Facebook can influence perceptions of status and success. Images of exotic vacations, designer clothes, and dinners at exclusive restaurants are used to build and maintain an image of prestige and sophistication. Social media not only amplifies the visibility of conspicuous consumption but also creates a cycle of desire and emulation among users.
Influences of Social Media on Luxury Goods Sales

For example, a Harvard University study found that luxury posts on Instagram can increase luxury product sales by 5% due to social influence. Celebrities and influencers play a crucial role in this process, with personalities like Kylie Jenner and Cristiano Ronaldo promoting high-end products that their followers aspire to own.
Causes of the Veblen Effect
Consumer Psychology
Psychology plays a crucial role in the Veblen Effect. Consumers seek to differentiate and stand out in society. Buying expensive and exclusive goods provides a sense of superiority and success. Social comparison theory suggests that people evaluate their own worth in relation to others, and consuming luxury goods can elevate one’s perception of themselves. Additionally, the “need to belong” phenomenon can motivate individuals to acquire products that allow them to be accepted in certain social circles.
A University of Chicago study revealed that 60% of luxury goods consumers buy these products to enhance their social image, while 40% do so for perceived quality. This data underscores how the desire for status and the perception of exclusivity are key drivers behind the Veblen Effect.
Exclusivity and Scarcity
Exclusivity and scarcity are key factors in the Veblen Effect. Luxury goods are often produced in limited quantities, which increases their appeal. The perceived scarcity of a product can make it more desirable, as consumers value harder-to-obtain objects more. Additionally, luxury brands invest in maintaining an image of exclusivity and prestige, reinforcing the Veblen Effect. Limiting availability and creating waitlists for certain products are common strategies used by brands to increase desire and demand.
For example, Hermès is known for its Birkin bags, which can cost from $10,000 to $150,000. The company produces these bags in very limited quantities and offers them only to selected customers, increasing their value and appeal. This approach has led to a consistent increase in demand for Birkins, despite their high prices.
Economic and Social Implications
Demand Elasticity
The Veblen Effect introduces complexities in demand elasticity. While most goods have negative price elasticity of demand, luxury goods can show positive elasticity in certain price ranges. This means that the relationship between price and demand is not linear and can change based on consumer perception. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for companies operating in the luxury goods market, as it influences pricing and marketing strategies.
Demand Elasticity in Luxury Goods
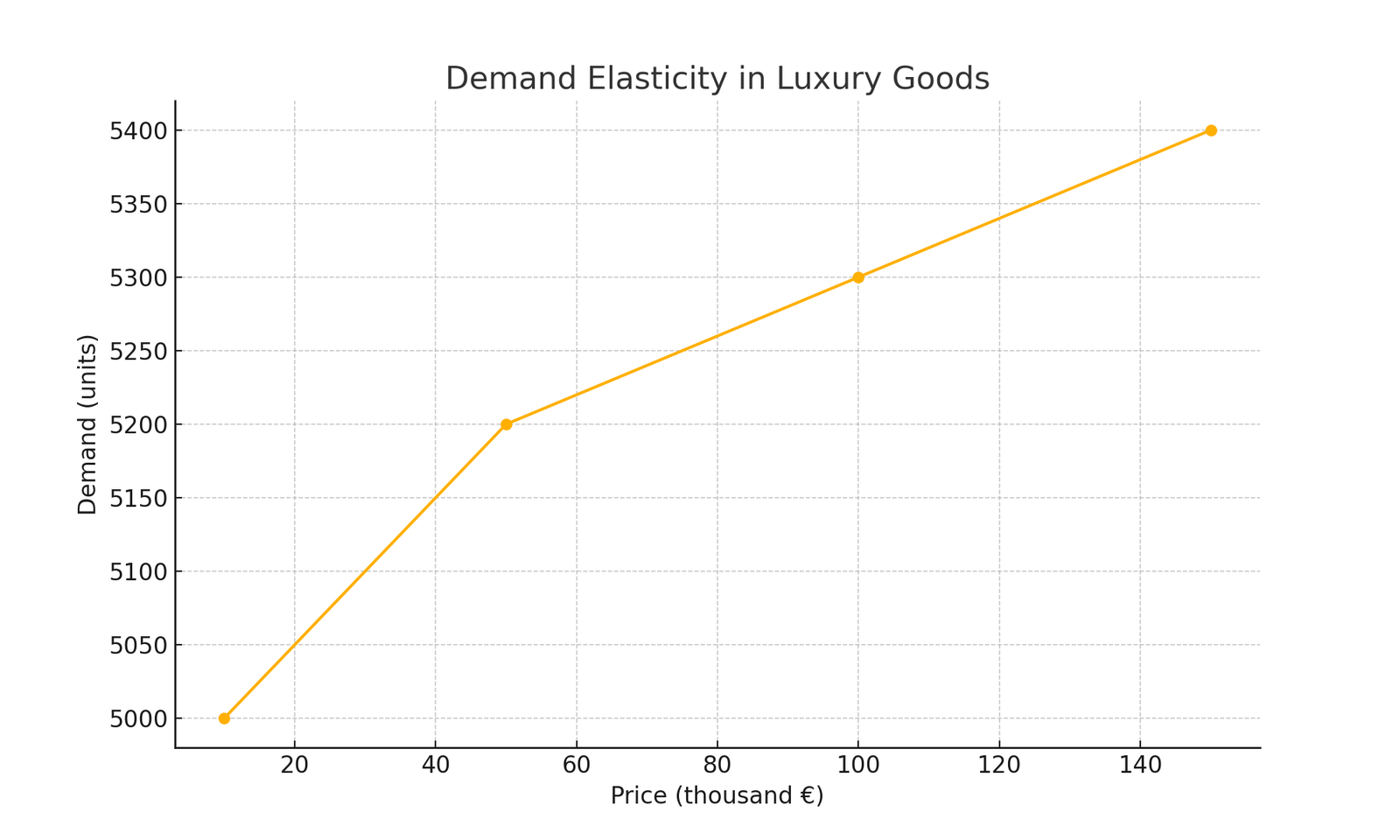
A Deloitte report from 2021 showed that 30% of luxury consumers are willing to pay more for products perceived as exclusive and high-quality. This data highlights how demand elasticity can be positive in the luxury goods market, challenging traditional expectations.
Economic Inequality
The Veblen Effect also reflects and reinforces economic inequality. Access to luxury goods is restricted to a high-income minority, which can exacerbate social divisions. Additionally, the desire to emulate the consumption of the upper classes can lead to unsustainable consumption behaviors among the middle and lower classes, fostering debt and financial stress. This imitation dynamic can perpetuate cycles of inequality and social exclusion as individuals try to maintain a status appearance beyond their economic reach.
According to data from the U.S. Federal Reserve, the richest 1% of the population owns 40% of the country’s total wealth. This concentration of wealth allows this group to access luxury goods, while the rest of the population may incur debt trying to emulate this lifestyle.
Relevance in the Modern Economy
Marketing and Brand Strategies
Luxury goods companies use the Veblen Effect in their marketing strategies. Advertising campaigns that emphasize exclusivity, unique design, and high quality help justify high prices and attract status-seeking consumers. Collaborations with celebrities and presence at exclusive events are also common tactics. Additionally, luxury brands often invest in creating exceptional and personalized shopping experiences for their customers, further reinforcing their perception of exclusivity.
A notable example is the watch brand Rolex, which uses brand ambassadors such as Roger Federer and Tiger Woods to promote its image of exclusivity and prestige. This strategy has allowed Rolex to maintain strong demand despite its high prices.
Impact on Global Trade
The luxury goods market has a significant impact on global trade. Countries like France, Italy, and Switzerland, known for their luxury brands in fashion, watchmaking, and wines, economically benefit from the worldwide demand for these products. Additionally, economic growth in emerging regions has created new markets for luxury consumption. Globalization and increasing purchasing power in countries like China and India have expanded the base of luxury goods consumers, transforming market dynamics and creating new opportunities and challenges for brands.
In 2022, China accounted for 35% of the global luxury goods market, according to a McKinsey & Company report. This growth has led Western luxury brands to establish a significant presence in the Chinese market, adapting their marketing strategies and products to attract local consumers.
Criticism and Controversies
Sustainability and Ethics
Conspicuous consumption and the Veblen Effect have been criticized from a sustainability and ethical perspective. The production and consumption of luxury goods often entail a high environmental cost. Additionally, the pursuit of status through consumption can be seen as frivolous and superficial, diverting resources from more urgent needs. The fashion industry, for example, faces criticism for its environmental impact and labor conditions in its supply chain. These concerns have led to a growing interest in sustainable luxury, where brands seek to balance prestige with social and environmental responsibility.
For example, Gucci has launched sustainability initiatives, committing to reduce its carbon footprint and use recycled materials in its products. This strategy not only addresses environmental criticisms but also attracts a new generation of environmentally conscious consumers.
Cultural Influence
The Veblen Effect also has cultural implications. In some societies, luxury consumption is seen as a manifestation of success and aspiration. However, in others, it may be criticized as a sign of decadence and materialism. These perceptions vary and evolve over time and globalization. In some contexts, the ostentation of luxury can be interpreted as a lack of sensitivity to social and economic inequalities. Additionally, the impact of globalization has led to a homogenization of status symbols, although local manifestations of conspicuous consumption can differ significantly.
A study by the University of Oxford found that in more collectivist cultures, such as those in East Asia, conspicuous consumption may be less socially accepted compared to more individualistic cultures, such as those in the United States and Western Europe. These cultural differences influence how luxury goods are perceived and adopted in different parts of the world.
Conclusion
The Veblen Effect is a complex phenomenon that challenges traditional economic laws and offers a window into the intricate relationship between consumption, status, and human psychology. Its relevance in the luxury goods market and its impact on the economy and society make it a continuous subject of study. Understanding this effect not only helps explain certain consumption behaviors but also provides valuable insights for formulating marketing strategies and economic policies. As the world continues to evolve, the study of the Veblen Effect will continue to offer crucial perspectives on the dynamics of consumption and the global economy.
Make a one-time donation
Make a monthly donation
Make a yearly donation
Choose an amount
Or enter a custom amount
Your contribution is appreciated.
Your contribution is appreciated.
Your contribution is appreciated.
DonateDonate monthlyDonate yearlyShare/Compártelo
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Threads (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- More
Related
Discover more from LUXONOMY
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.














